The Feed service provides delivery of data feeds based on underlying services across the Piksel Video Platform.
It allows for the following features over and above standard API access:
- Query Management: Feeds provide common query configurations, allowing multiple clients to make use of the same query and provide central point for updates and management of a given feed.
- Curated lists: Feeds may be configured for a particular purpose, such as items for a carousel, latest offers display etc.
- Restricted data: Feeds allow for the data returned to be restricted ensuring that only data needed for the purpose of the feed is made available.
- Overridable: Query parameter overrides may be supplied in the feed URL to further refine the feed response (provided they restrict the result set further)
- High Performance and Availability: Feed specific server-side caching policies ensure that the Feed service can provide high performance and high availability access to feeds.
- Shorter URLs: The Feed service allows for shorter, more comprehensible feed URLs.
- Unauthenticated public access: Some clients may not support complex authentication flows or do not want to deal with the overhead of handling access tokens.
Conversely, it should not be used if:
- Up-to-date information is required - server-side caching adds a delay
- Full control over query parameters is a requirement - public caching of all data is usually not desired
The following services may be used by Feed:
In addition to this user guide, full reference docs are available here.
Concepts
Feed Anatomy
Feeds are structured as follows:
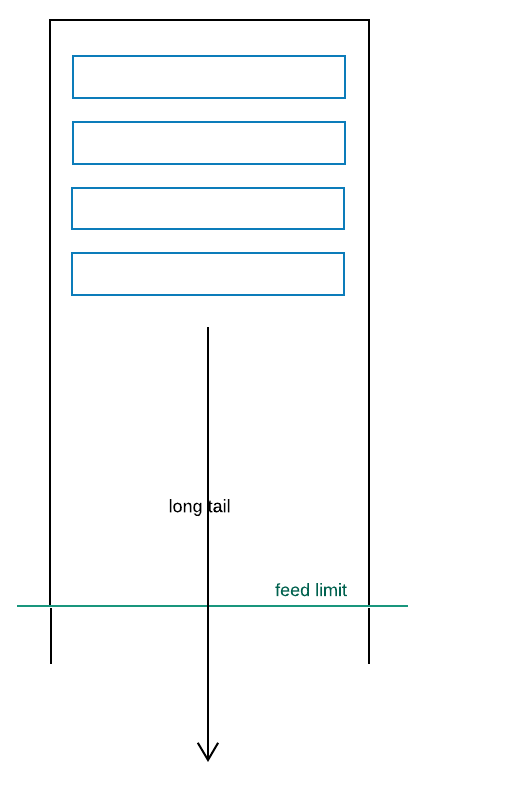
- The
ownerof the feed determines theownerin the upstream services - A feed can optionally have a maximum length to ensure that clients do not exhaustively query
Layered Architecture
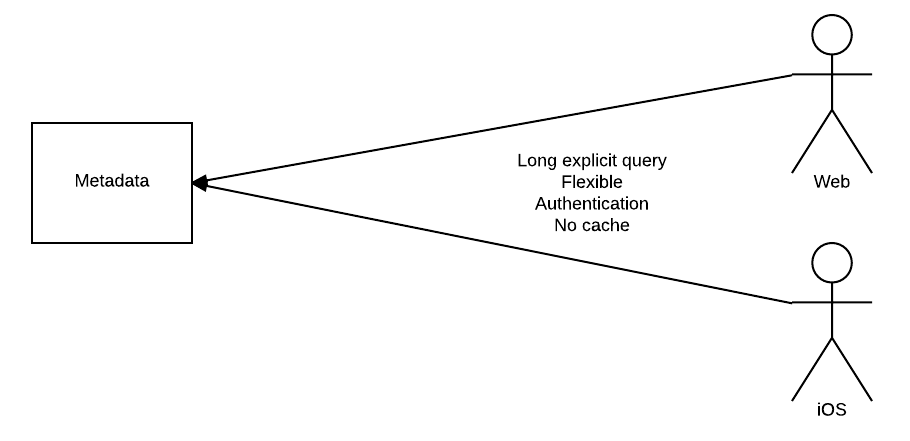
Ordinarily, clients may interact with the Metadata service directly and have full control over discovering data, however, in doing so they must be authorised and there is no caching or ability to share common queries.
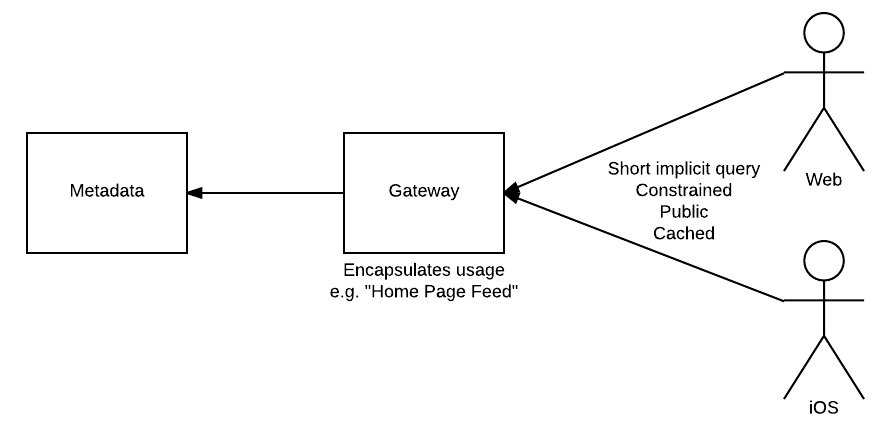
Consumer Apps typically make very similar queries that need to be highly performant. Making use of Feed service in front of Metadata service allows for unauthenticated, cacheable, common base queries with predefined extensibility.
Feed configuration
Overview
Feed configs define how the feed should be constructed including the service, resource, owner, and the query params for the upstream calls e.g. fields, filters.
The owner in the feedConfig also defines the owner of the resources in the upstream service.
Feed configs are divided into defaults and optional sections.
When no query parameters are present, the values from defaults are used to create the feed. Query parameter overrides can be chosen from both defaults and optional
Feeds are public and as such are designed to give restricted access to upstream services. The config explicitly specify which resources may be included in the feed. Feeds don’t rely on service defaults (e.g. default field set) as they may change, inadvertently exposing those changes in the feed.
When customising feeds, overriding query params cannot expand the result set further than what is defined in the feed config. fields, count and sort can be chosen from default + optional. (NB: Sort overrides may disregard asc/desc sort order). The filters parameter is additive and not overrideable, resulting in filters with the same name applied with an && relationship.
Filters allow the use of the operators || and && to indicate logical disjunction and conjunction between values e.g. withTags=api&&json means both tags need to be present, withType=show||episode means the pieces of content returned can be of either type.
Filters may use time-based fields, which may naturally require using the current time (i.e. the time the feed is requested). The following syntax allows defining relative time: {NOW}, {NOW-P1D} and {NOW+P1D} meaning current time, 1 day ago and 1 day from now respectively.
Example feed config
{
"owner": "test",
"name": "popular-shows",
"title": "Popular shows",
"service": "metadata",
"type": "contents",
"count": "true",
"perPage": "100",
"limit": 100,
"lang": "en",
"fields": ["ref", "title"],
"dynamicContent": {
"enabled": true,
"filters": {
"withAvailabilityStartAt": "{NOW}/{NOW+P20D}",
"withTitle": "The Walking Dead||Game of Thrones"
},
"sort": ["-createdAt"]
},
"consumerParameters": {
"overrides": {
"count": ["active","type"],
"fields": ["active"],
"sort": ["title"]
},
"appends": {
"filters": ["withTitle"]
}
},
"cachePolicy": {
"ttl": "PT5M"
}
}
An up-to-date description of all feed config options are found in the service API documentation.
Permissions
The following permissions are required to read/write feed configs. (NB: Accessing the feed business endpoint does not require any features/permissions.)
feed:feed-configs:read(to read)feed:feed-configs:write(to write)
The following feature in the tenancy in question also required:
root:feed-management
Consumption
The feed business endpoint: https://{feed}/f/{owner}/{name}.
owner and name are the respective fields of the feedConfig resource defining the feed.
The endpoint is public and highly available through server-side caching (via Varnish) with built-in cache stampede protection. Caching can be configured via the ttl setting under cachePolicy within the feedConfig. The ttl is a seconds value which defines the window of time in which a cached resource can be served to a client. We utilise the s-maxage, stale-while-revalidate and stale-if-error Cache-Control header values as defined in RFC5861.
The consumption examples below use the feed config from the previous section.
Error codes
The following error codes are returned from the business endpoint
| Status Code | Message | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 400 | Bad Request | The query string contains disallowed parameters |
| 404 | Not Found | The feedConfig doesn’t exist |
| 502 | Bad Gateway | Error in the upstream request, may indicate a problem with the feedConfig |
Example 1: Defaults
Query:
GET https://{feed}/f/test/popular-shows
Equivalent direct query:
GET https://{metadata}/data/contents?fields=ref,title&sort=-createdAt&count=true&owner=test&withTitle=The%20Walking%20Dead||Game%20of%20Thrones&page=1&withType=show&perPage=100
Result:
{
"meta": {
"totalCount": 2,
"page": 1,
"perPage": 100
},
"contents": [
{
"ref": "test:the-walking-dead",
"title": "The Walking Dead"
},
{
"ref": "test:game-of-thrones",
"title": "Game of Thrones"
}
]
}
Example 2: Overriding fields and sort
Query:
GET https://{feed}/f/test/popular-shows?fields=title,active&sort=title
Equivalent direct query:
GET https://{metadata}/data/contents?fields=title,active&sort=title&count=true&owner=test&withTitle=The%20Walking%20Dead||Game%20of%20Thrones&page=1&withType=show&perPage=100
Result:
{
"meta": {
"totalCount": 2,
"page": 1,
"perPage": 100
},
"contents": [
{
"title": "Game of Thrones",
"active": true
},
{
"title": "The Walking Dead",
"active": true
}
]
}
Example 3: Adding extra filter
Query:
GET https://{feed}/f/test/popular-shows?withTitle=The%20Walking%20Dead
Equivalent direct query:
GET https://{metadata}/data/contents?fields=ref,title&sort=-createdAt&count=true&owner=test&withTitle=The%20Walking%20Dead&withTitle=The%20Walking%20Dead||Game%20of%20Thrones&page=1&withType=show&perPage=100
Note that both the original and the new filter is applied.
Result:
{
"meta": {
"totalCount": 2,
"page": 1,
"perPage": 100
},
"contents": [
{
"ref": "test:the-walking-dead",
"title": "The Walking Dead"
}
]
}